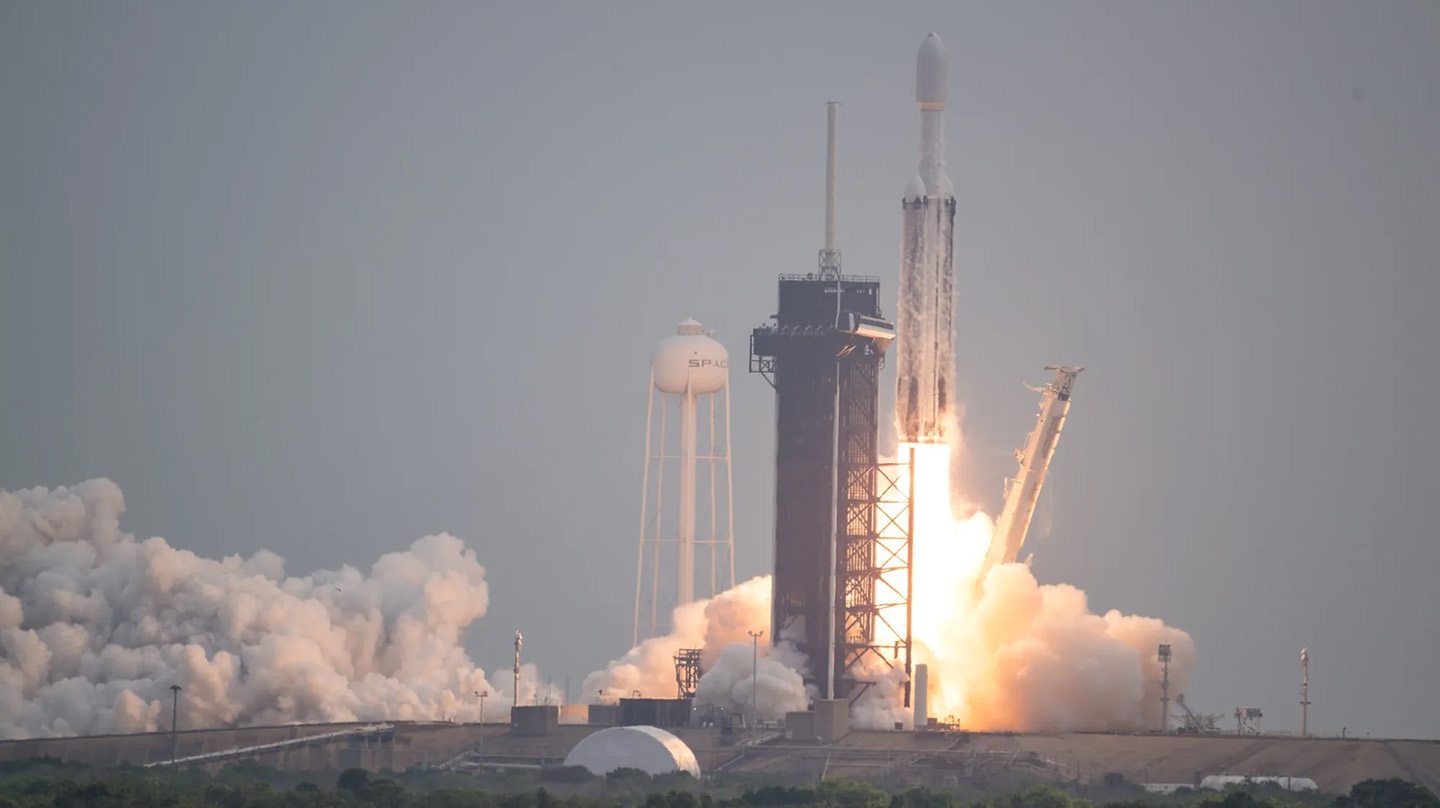
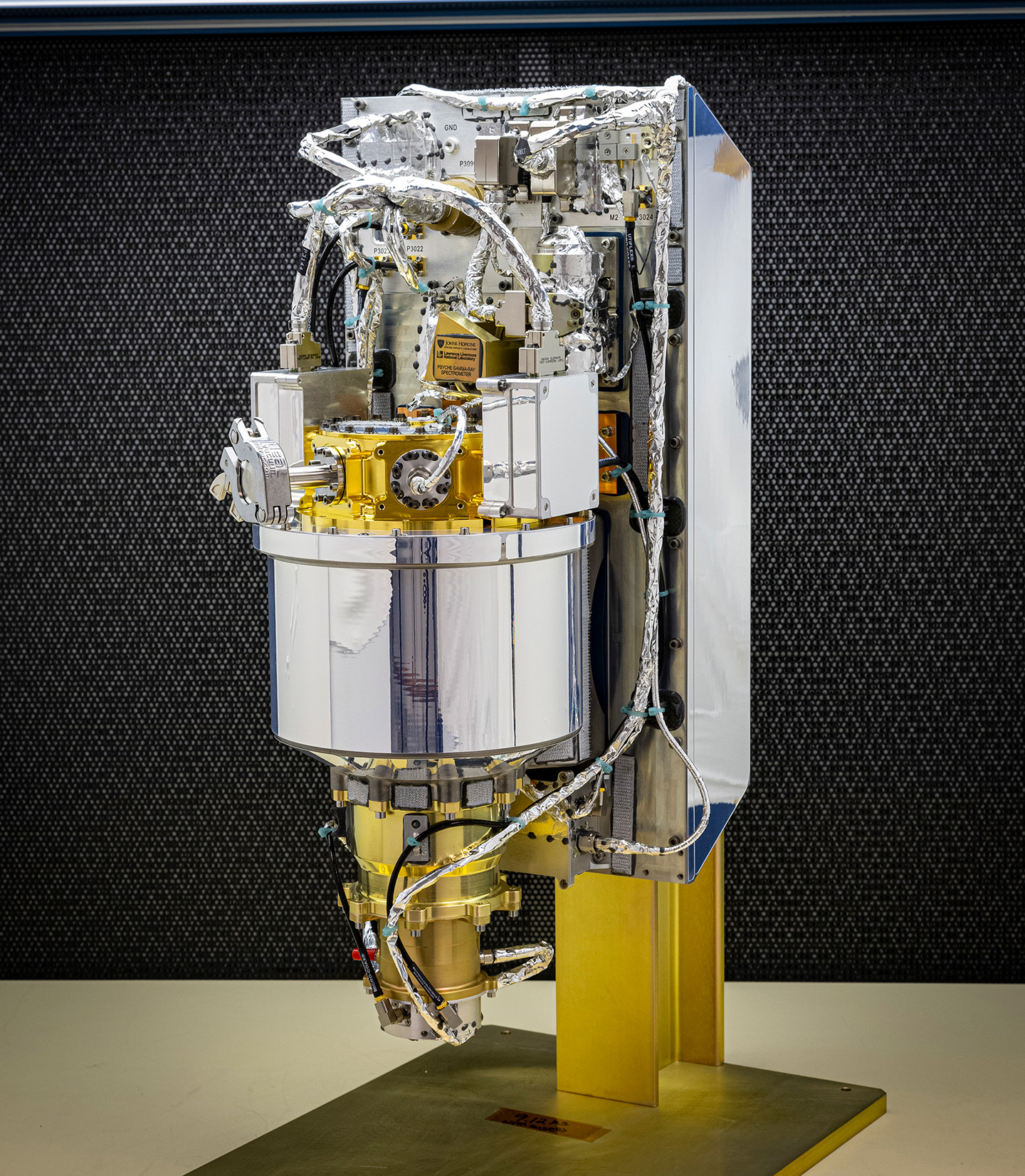
NASA’s Psyche spacecraft, the first mission sent to study a potentially metal-rich asteroid, launched on Oct. 13 carrying a Gamma-Ray and Neutron Spectrometer (GRNS) developed at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland.

Psyche lifted off from Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket. At 150 miles (240 kilometers) in diameter, its target, the asteroid Psyche (pronounced SIGH-kee), could be the largest of a class of metal-rich asteroids in the solar system. Scientists suspect these asteroids may be shards of early protoplanetary cores like the one inside Earth.
The GRNS will play a key role in Psyche’s mission by revealing the asteroid’s composition — and, in turn, its possible planetary history. The instrument uses cosmic-ray protons, a stream of high-velocity protons created by stellar explosions outside the solar system, that strike the asteroid, stimulating the release of gamma rays and neutrons.
“APL teams continue to push the envelope and develop reliable, cutting-edge scientific instruments to better understand our solar system — and beyond,” said Andy Driesman, APL’s mission area executive for Civil Space Flight. “We’re excited for APL technology to fly aboard NASA’s Psyche spacecraft in partnership with Arizona State University and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. We can’t wait to share this critical data with researchers around the world.”
The instrument consists of a gamma-ray spectrometer (GRS) and neutron spectrometer (NS). The GRS will capture gamma rays to quantify the asteroid’s elemental composition. The NS will provide information on Psyche’s metal composition — as well as on the presence of other potential elements such as hydrogen — to complement the gamma-ray data.
A Long Road Ahead
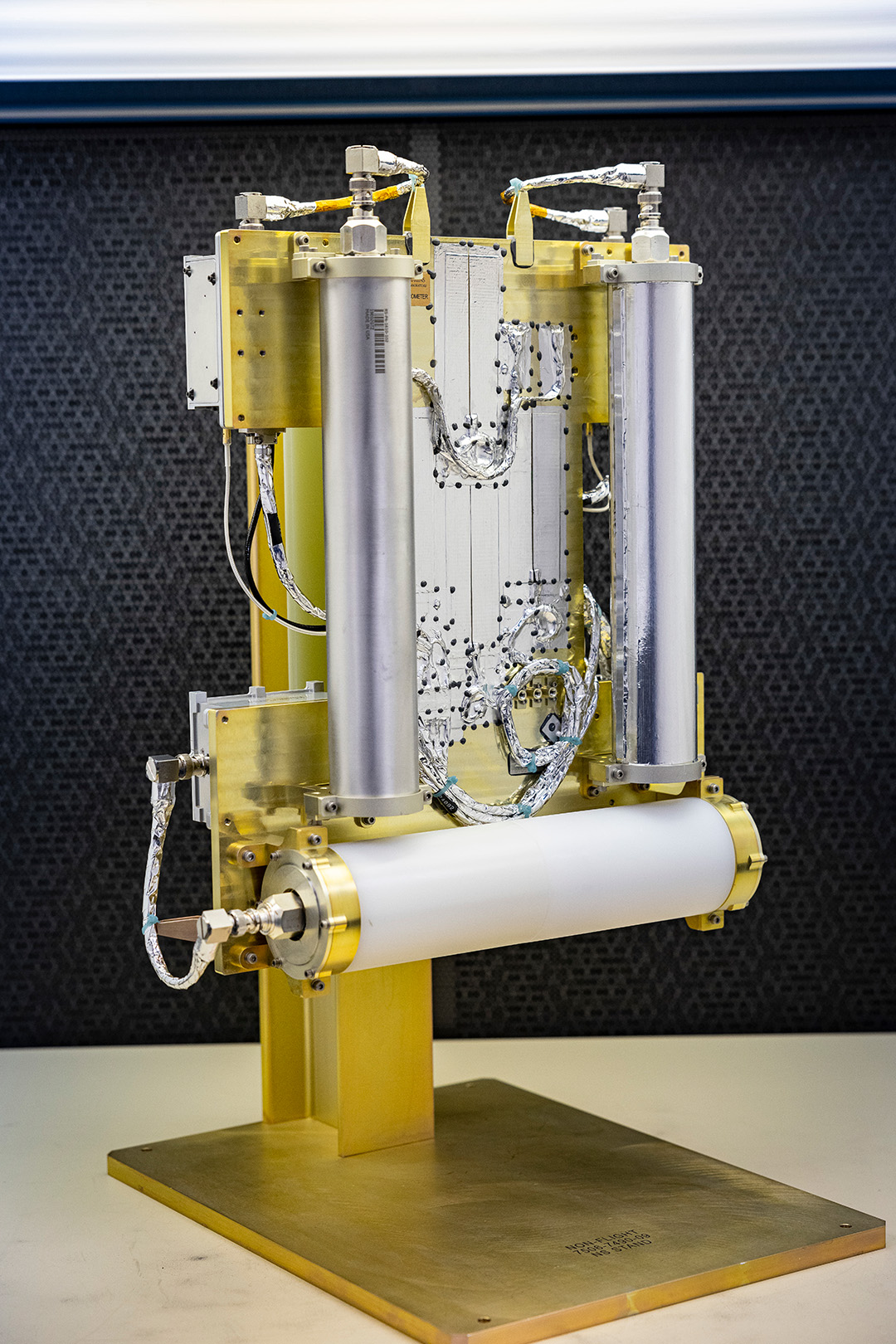
After five years of testing and development, the GRNS shipped to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, in 2021 in preparation for launch.
“We are so excited to see our instrument launch,” said David Lawrence, a planetary scientist at APL and lead investigator of the GRNS. “It took a lot of hard work from a dedicated team at APL and our partner institutions to get to this point, and we’re more than ready for the mission’s next stage.”
The voyage to Psyche will last nearly six years and navigate approximately 2.2 billion miles (3.6 billion kilometers). The spacecraft will reach the asteroid in 2029, where it will orbit for over two years. In mid-2030 it will arrive within 60 miles (100 kilometers) of the surface, after which it will take around 100 days to collect sufficient data.
Once scientists have enough data, they can determine what makes up the surface of the asteroid.
“This work rewards those who are patient,” Lawrence said.
The next key step for GRNS happens roughly 45 days from launch, when APL scientists will turn on the instrument for the first time.
A History of Collaboration
APL has decades of experience building GRNS instruments, including for NASA’s Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous (NEAR) mission to study the asteroid Eros in the 1990s, and the agency’s MESSENGER mission to Mercury, which provided key discoveries about the planet’s composition and critical details about how our solar system was formed. The Psyche GRNS’s design leverages the Laboratory’s experience while also incorporating recent technological advancements, including the use of a miniature cryocooler. Similar instruments are planned for flight to Mars’ moon Phobos aboard Japan’s Martian Moons eXploration (MMX) mission and to Titan as part of the NASA Dragonfly mission.
Arizona State University leads the Psyche mission. A division of Caltech in Pasadena, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory is responsible for the mission’s overall management, systems engineering, integration and test, and mission operations.
To learn more about Psyche and the GRNS, visit https://www.nasa.gov/psyche and https://space.jhuapl.edu/destinations/instruments/psyche-grns.
Related Topics
Science
For Media Inquiries
For all media inquiries, including permission to use images or video in our gallery, please contact:
Michael Buckley
All Media Resources

